If you or a loved one experiences anxiety or fear when going to the dentist, IV sedation can help. Working with a dental anesthesiologist enables even the youngest of patients safe and comfortable oral health care.
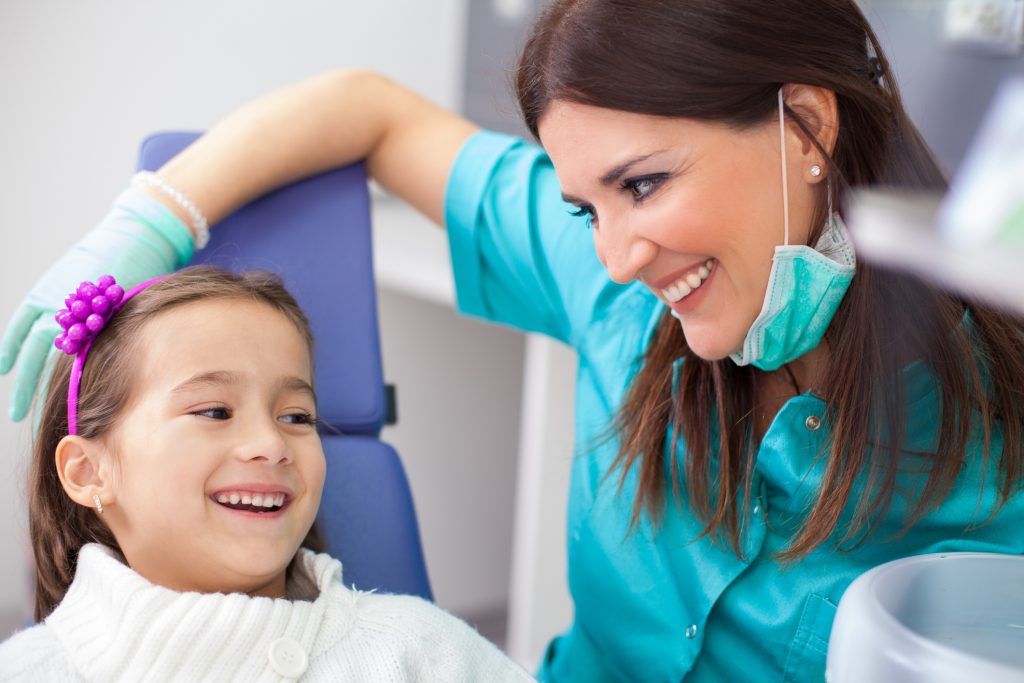 There is no need to put your loved one through a taxing situation or unnecessary distress for an extraction or root canal, or even a cleaning. There are a number of choices when it comes to comforting a loved one while at the dentist. IV sedation is a safe and effective for anyone to have a relaxing experience at the dentist.
There is no need to put your loved one through a taxing situation or unnecessary distress for an extraction or root canal, or even a cleaning. There are a number of choices when it comes to comforting a loved one while at the dentist. IV sedation is a safe and effective for anyone to have a relaxing experience at the dentist.
IV sedation is administered to the patient, both children and adults, to help relieve the stress and anxiety.
Though IV sedation reduces the patient’s consciousness, they are in a semi-awake state, opposed to being asleep. It is a controllable level, which makes it safe and effective.
When it comes to IV Sedation you want to take all the necessary safety precautions. Which is why it is important to have a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist present, to monitor the patients vitals and administer the sedation. This way the dentist is able to concentrate fully on the treatment, while the CRNA is focusing only on the patient safety, vigilance, and monitoring.
According to the American Society of Dentist Anesthesiologists, having anesthesia helps both children and adults, from all walks of life, get the dental care they deserve, from routine cleanings to restorative procedures.
Children
Sedating or anesthetizing kids demands highly specialized expertise. A Dentist Anesthesiologist can help if your child is:
Too young to cooperate
Needs a lot of dental care
Is extremely fearful
Adult Patients
These are a few of the most common reasons why adults need a Dentist Anesthesiologist:
Fear of seeing a dentist
Difficulty getting or staying numb
Needing extensive dental work
Strong gag reflex
Anyone undergoing oral surgery or any major facial/jaw surgery
Special Needs
Many patients have physical or intellectual challenges that make it difficult to get dental care. These include:
Developmental disabilities
Autism
Down syndrome
Dementia or Alzheimer’s
Parkinson’s disease
Cerebral palsy
Psychiatric conditions